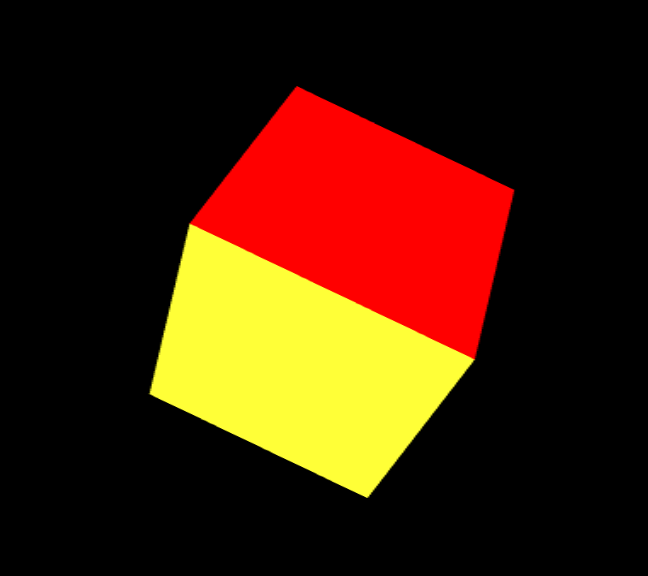
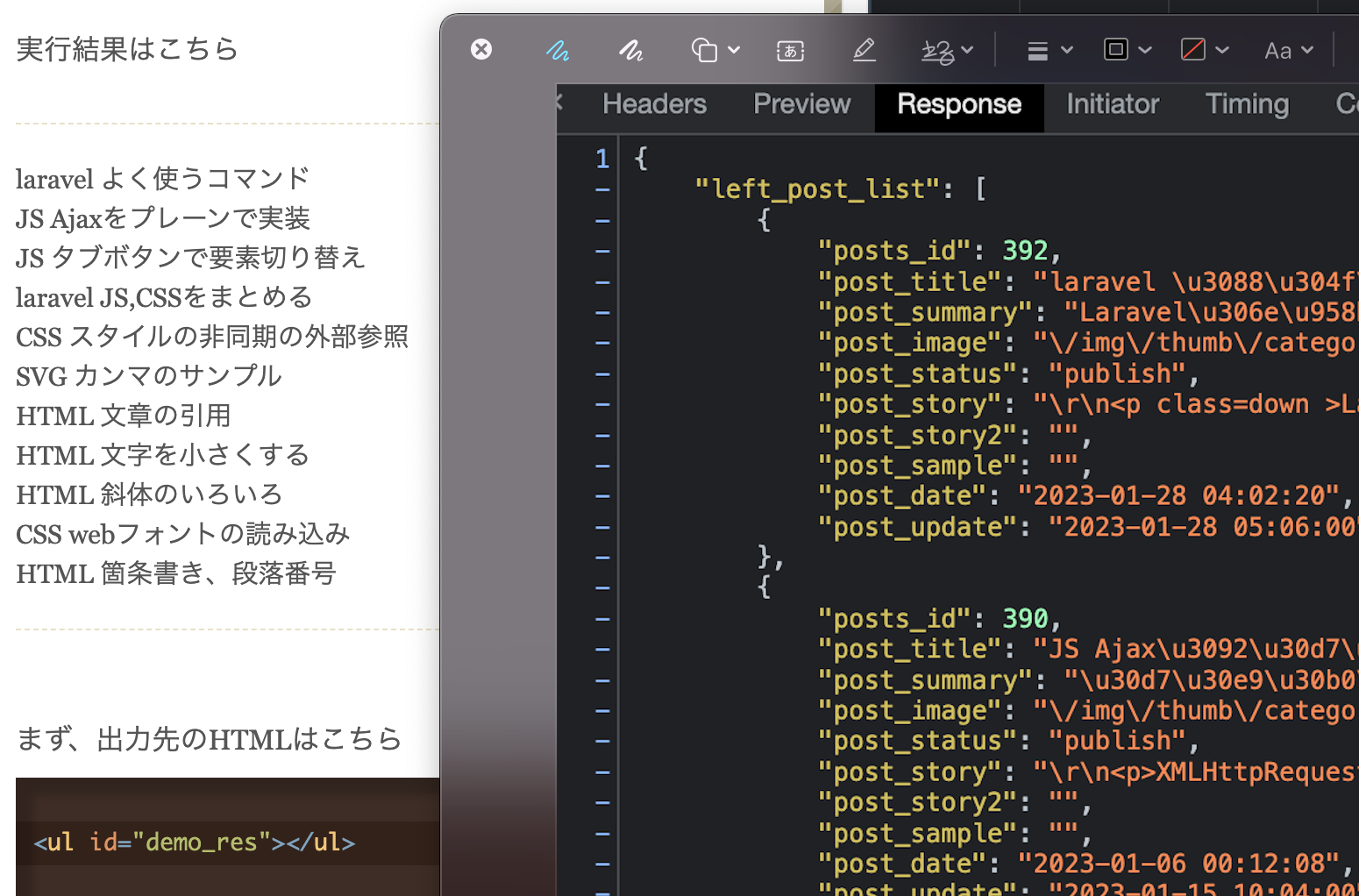
参考サイトMDNを参考にサンプルをそのまま実装してみました。
まだ、筆者も理解が浅いので、今日はここまでです。
下記のサイトを参考にしています。
https://developer.mozilla.org/ja/docs/Web/API/WebGL_API/Tutorial/Animating_objects_with_WebGLHTMLはこちら
<canvas id="demo_cnvs" width="1500" height="1500"></canvas>
読み込むライブラリは gl-matrix-min.js です。
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/gl-matrix/2.8.1/gl-matrix-min.js"></script>canvasの横幅を1500pxにして、スタイルで横幅を100%にしています。
#demo_cnvs {
border: 2px solid black;
background-color: black;
width:100%;
height:300px;
}
video {
display: none;
}こうしないと画質が荒くなるようです。
var cubeRotation = 0.0;
main();
//
// Start here
//
function main() {
const canvas = document.querySelector('#demo_cnvs');
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
// If we don't have a GL context, give up now
if (!gl) {
alert('Unable to initialize WebGL. Your browser or machine may not support it.');
return;
}
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec4 aVertexPosition;
attribute vec4 aVertexColor;
uniform mat4 uModelViewMatrix;
uniform mat4 uProjectionMatrix;
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = uProjectionMatrix * uModelViewMatrix * aVertexPosition;
vColor = aVertexColor;
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vColor;
}
`;
// Initialize a shader program; this is where all the lighting
// for the vertices and so forth is established.
const shaderProgram = initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource);
// Collect all the info needed to use the shader program.
// Look up which attributes our shader program is using
// for aVertexPosition, aVevrtexColor and also
// look up uniform locations.
const programInfo = {
program: shaderProgram,
attribLocations: {
vertexPosition: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexPosition'),
vertexColor: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexColor'),
},
uniformLocations: {
projectionMatrix: gl.getUniformLocation(shaderProgram, 'uProjectionMatrix'),
modelViewMatrix: gl.getUniformLocation(shaderProgram, 'uModelViewMatrix'),
}
};
// Here's where we call the routine that builds all the
// objects we'll be drawing.
const buffers = initBuffers(gl);
var then = 0;
// Draw the scene repeatedly
function render(now) {
now *= 0.001; // convert to seconds
const deltaTime = now - then;
then = now;
drawScene(gl, programInfo, buffers, deltaTime);
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
//
// initBuffers
//
// Initialize the buffers we'll need. For this demo, we just
// have one object -- a simple three-dimensional cube.
//
function initBuffers(gl) {
// Create a buffer for the cube's vertex positions.
const positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
// Select the positionBuffer as the one to apply buffer
// operations to from here out.
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);
// Now create an array of positions for the cube.
const positions = [
// Front face
-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
// Back face
-1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
// Top face
-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
// Bottom face
-1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
// Right face
1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
// Left face
-1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
];
// Now pass the list of positions into WebGL to build the
// shape. We do this by creating a Float32Array from the
// JavaScript array, then use it to fill the current buffer.
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(positions), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Now set up the colors for the faces. We'll use solid colors
// for each face.
const faceColors = [
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0], // Front face: white
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0], // Back face: red
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0], // Top face: green
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0], // Bottom face: blue
[1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0], // Right face: yellow
[1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0], // Left face: purple
];
// Convert the array of colors into a table for all the vertices.
var colors = [];
for (var j = 0; j < faceColors.length; ++j) {
const c = faceColors[j];
// Repeat each color four times for the four vertices of the face
colors = colors.concat(c, c, c, c);
}
const colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(colors), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Build the element array buffer; this specifies the indices
// into the vertex arrays for each face's vertices.
const indexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexBuffer);
// This array defines each face as two triangles, using the
// indices into the vertex array to specify each triangle's
// position.
const indices = [
0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3, // front
4, 5, 6, 4, 6, 7, // back
8, 9, 10, 8, 10, 11, // top
12, 13, 14, 12, 14, 15, // bottom
16, 17, 18, 16, 18, 19, // right
20, 21, 22, 20, 22, 23, // left
];
// Now send the element array to GL
gl.bufferData(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,
new Uint16Array(indices), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
return {
position: positionBuffer,
color: colorBuffer,
indices: indexBuffer,
};
}
//
// Draw the scene.
//
function drawScene(gl, programInfo, buffers, deltaTime) {
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // Clear to black, fully opaque
gl.clearDepth(1.0); // Clear everything
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST); // Enable depth testing
gl.depthFunc(gl.LEQUAL); // Near things obscure far things
// Clear the canvas before we start drawing on it.
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Create a perspective matrix, a special matrix that is
// used to simulate the distortion of perspective in a camera.
// Our field of view is 45 degrees, with a width/height
// ratio that matches the display size of the canvas
// and we only want to see objects between 0.1 units
// and 100 units away from the camera.
const fieldOfView = 45 * Math.PI / 180; // in radians
const aspect = gl.canvas.clientWidth / gl.canvas.clientHeight;
const zNear = 0.1;
const zFar = 100.0;
const projectionMatrix = mat4.create();
// note: glmatrix.js always has the first argument
// as the destination to receive the result.
mat4.perspective(projectionMatrix,
fieldOfView,
aspect,
zNear,
zFar);
// Set the drawing position to the "identity" point, which is
// the center of the scene.
const modelViewMatrix = mat4.create();
// Now move the drawing position a bit to where we want to
// start drawing the square.
mat4.translate(modelViewMatrix, // destination matrix
modelViewMatrix, // matrix to translate
[-0.0, 0.0, -6.0]); // amount to translate
mat4.rotate(modelViewMatrix, // destination matrix
modelViewMatrix, // matrix to rotate
cubeRotation, // amount to rotate in radians
[0, 0, 1]); // axis to rotate around (Z)
mat4.rotate(modelViewMatrix, // destination matrix
modelViewMatrix, // matrix to rotate
cubeRotation * .7,// amount to rotate in radians
[0, 1, 0]); // axis to rotate around (X)
// Tell WebGL how to pull out the positions from the position
// buffer into the vertexPosition attribute
{
const numComponents = 3;
const type = gl.FLOAT;
const normalize = false;
const stride = 0;
const offset = 0;
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffers.position);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
programInfo.attribLocations.vertexPosition,
numComponents,
type,
normalize,
stride,
offset);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(
programInfo.attribLocations.vertexPosition);
}
// Tell WebGL how to pull out the colors from the color buffer
// into the vertexColor attribute.
{
const numComponents = 4;
const type = gl.FLOAT;
const normalize = false;
const stride = 0;
const offset = 0;
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffers.color);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
programInfo.attribLocations.vertexColor,
numComponents,
type,
normalize,
stride,
offset);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(
programInfo.attribLocations.vertexColor);
}
// Tell WebGL which indices to use to index the vertices
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, buffers.indices);
// Tell WebGL to use our program when drawing
gl.useProgram(programInfo.program);
// Set the shader uniforms
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(
programInfo.uniformLocations.projectionMatrix,
false,
projectionMatrix);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(
programInfo.uniformLocations.modelViewMatrix,
false,
modelViewMatrix);
{
const vertexCount = 36;
const type = gl.UNSIGNED_SHORT;
const offset = 0;
gl.drawElements(gl.TRIANGLES, vertexCount, type, offset);
}
// Update the rotation for the next draw
cubeRotation += deltaTime;
}
//
// Initialize a shader program, so WebGL knows how to draw our data
//
function initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource) {
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl, gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl, gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// If creating the shader program failed, alert
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
alert('Unable to initialize the shader program: ' + gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram));
return null;
}
return shaderProgram;
}
//
// creates a shader of the given type, uploads the source and
// compiles it.
//
function loadShader(gl, type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
// Send the source to the shader object
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
// Compile the shader program
gl.compileShader(shader);
// See if it compiled successfully
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
alert('An error occurred compiling the shaders: ' + gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader));
gl.deleteShader(shader);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
スクリプトの解析は今後やっていきたいと思います。